Logistic regression and support vector machine (SVM) are both popular models that can be applied to classification tasks. This article gives the introduction of these two methods and summarizes the differences between them.
What is Logistic Regression?
Logistic regression is a generalized linear model for binary classification. In logistic regression, we take the output of the linear function and then pass the value to the sigmoid function. The sigmoid function is S-shaped, it is a bounded and differentiable activation function. We use sigmoid function in logistic regression because it can take any real-valued number and map it into a value between the range of 0 and 1, as is known to all, the probability of any event is between 0 and 1, so sigmoid function is an intuitive and right choice for logistic regression. After we get the probabilities, we then set a threshold to make decisions, if the probability is greater than the threshold, we assign it a label 1, else we assign it a label 0.
What is Support Vector Machine (SVM)?
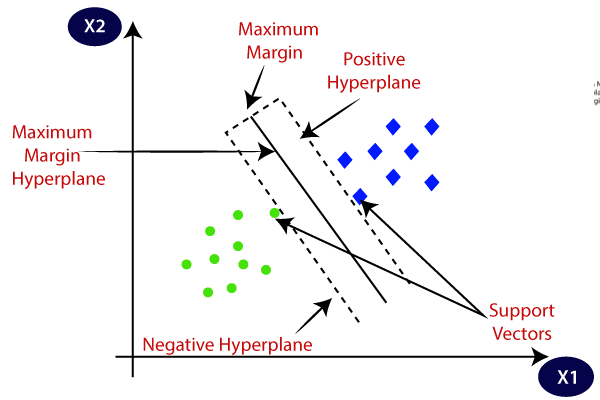
What's the difference between logistic regression and support vector machine?
- They are different in loss function. Logistic regression minimize log loss function while SVM minimizes hinge loss function.
- When we have a perfect linearly separable dataset, SVM can easily find the optimal hyperplane and all the data points can be classified correctly, while logistic regression will have difficulty to converge, thus failing to make classifications.
- Logistic regression is more sensitive to outliers than SVM.
- Because logistic regression finds its boundary by including all the data, so some outliers can make a difference to the boundary.
- SVM finds its maximal margin hyperplane by several support vectors that lie along the lines indicating the width of the maximal margin, so outliers that are far away from the margin have no effects on its decision boundary.
- SVM do not directly provide probabilities (values between 0 and 1), while logistic regression can easily produce probabilities.
- This might be a good property for logistic regression when what we want is an estimation, instead of absolute predictions, or when we don't have enough confidence into the data.
- SVM is more flexible than logistic regression.
- With different kernels (RBF, POLY, etc), SVM can learn different patterns in a non-linear dataset, however, it can be tricky to find the most appropriate kernel sometimes.
- Logistic regression assumes linearity between the log odds of an event occurring and predictor variables, so it may not perform well when we have a complex non-linear dataset.
- SVM woks better for high dimensional data.
- SVM is computationally efficient (with kernel tricks), especially when working with higher dimensional spaces.
- SVM works well with unstructured and semi-structured data (like text and images), while logistic regression works with already identified independent variables.

Thanks for writing this up, I really like this!
ReplyDelete: )
Delete